Summary
-
EMV is a payment method based on a technical standard for smart payment cards and payment terminals/ATM’s that accept them. EMV specification is governed by EMVCo, joint owned by the major card issuers around the world.
-
EMV cards have smart cards/integrated circuits which store their data on the chip (in addition to the magnetic stripe). These cards make use of physical insertion mechanisms and contactless pay methods using NFC to communicate with a Point-of-Service terminal.
-
EMV enables two verification methods:
- Chip and PIN
- Chip and signature
-
POS System Model using EMV:
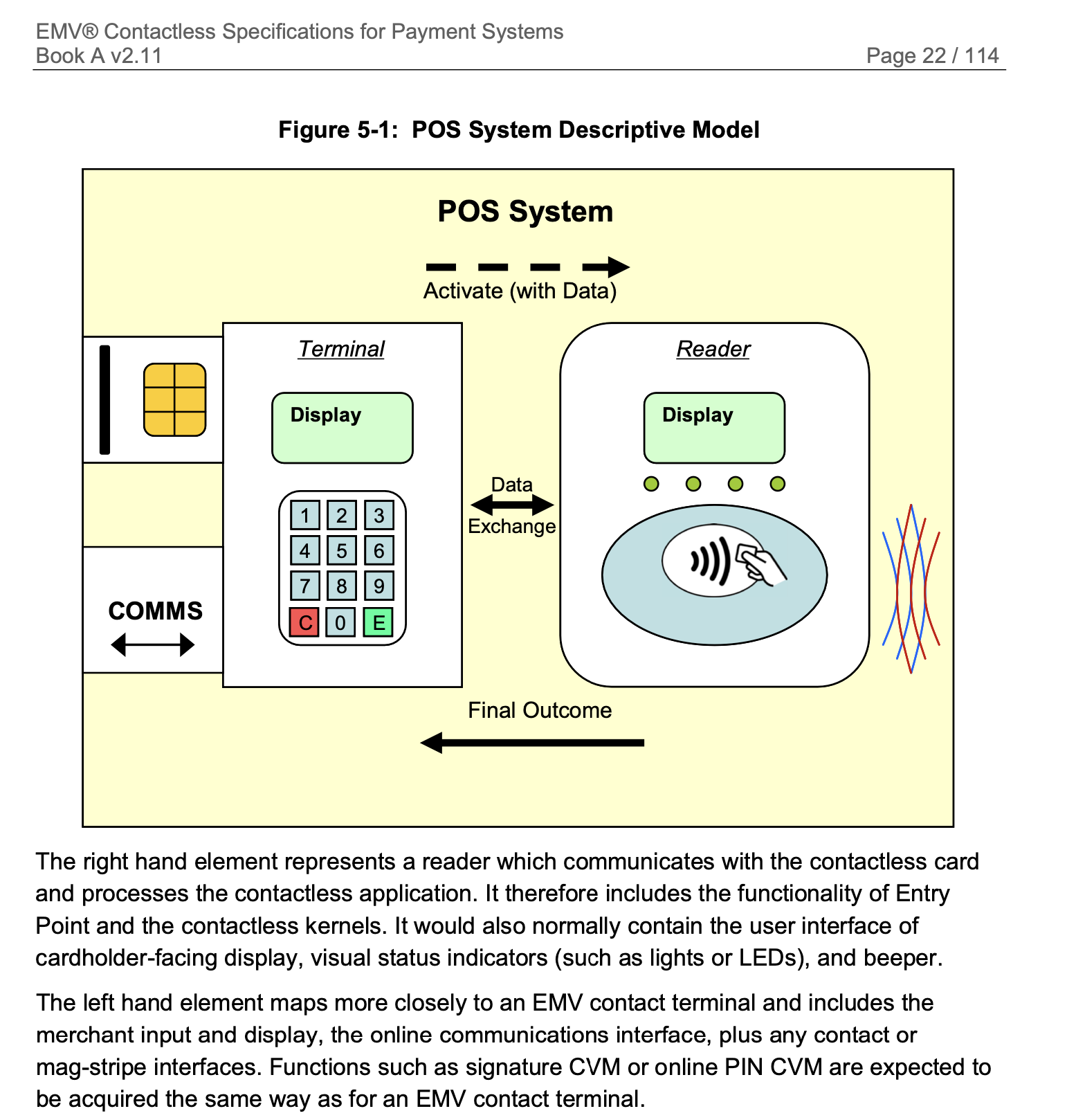
- Reader responsibilities:
- communication with contactless cards
- application selection and kernel activation
- running the contactless kernel applications
- management of a “no card response” timeout
- management of the contactless field
- Terminal responsibilities:
- provision of data entry (amount) by the merchant
- processing of Final Outcomes, including the handling of authorisation requests and responses
- cardholder verification (unless delegated to a cardholder device, such as a mobile phone)
- communication for authorisation messages and clearing records, using mag-stripe or chip-based data
- transactions on other interfaces (contact and mag-stripe)
- other aspects of transaction processing, including timeouts and cancellations
- Reader responsibilities:
- EMV POS Logical Architecture:
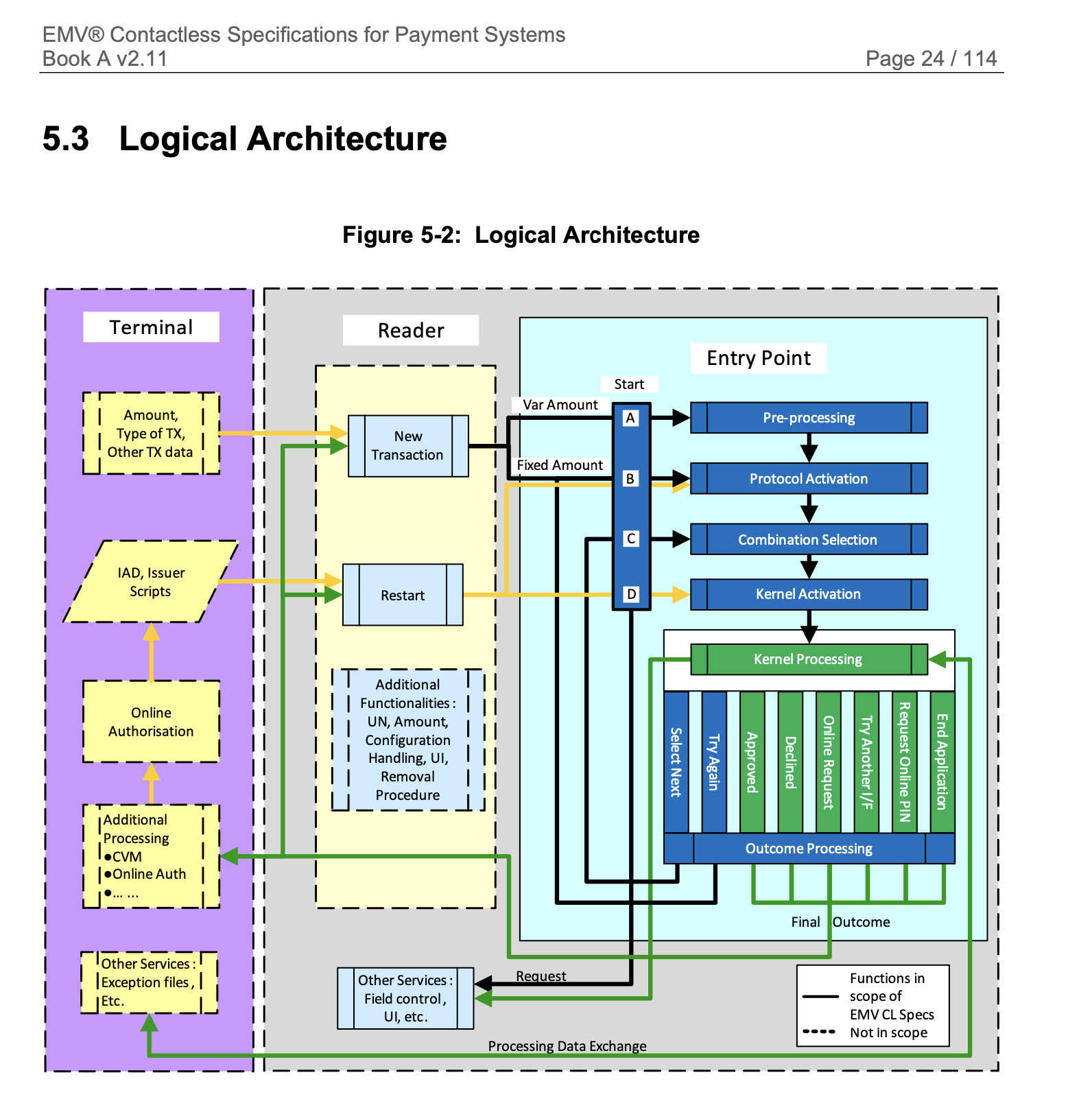
-
Standards/Specifications for EMV
- Contactless Specifications:
- Book A: Architecture and General Requirements
- Book B: Entry Point Specification
- Book C-2: Kernel 2 Specification
- Book C-3: Kernel 3 Specification
- Book C-4: Kernel 4 Specification
- Book C-5: Kernel 5 Specification
- Book C-6: Kernel 6 Specification
- Book C-7: Kernel 7 Specification
- Book C-8: Kernel 8 Specification
- Book E: Security and Key Management
- EMV Documents:
- Book 1: Application Independent ICC to Terminal Interface Requirements
- Book 2: Security and Key Management
- Book 3: Application Specification
- Book 4: Cardholder, Attendant, and Acquirer Interface Requirements
- The following ISO Standards apply to EMV:
- ISO 639-1: Codes for the representation of names of languages – Part 1: Alpha-2 Code.
- ISO 4217: Codes for the representation of currencies and funds.
- ISO 14443-3: Identification cards – Contactless integrated circuit(s) cards – Proximity cards – Part 3: Initialization and anticollision
- ISO/IEC 8859: Information Processing – 8-bit Single-Byte Coded Graphic Character Sets.
- Contactless Specifications: